ROS 2机器人自动充电之雷达点云法
-
ROS 2机器人自动充电之雷达点云法
前言
大家好,我是小鱼。最近我在折腾一个户外机器人项目,由于这个项目需要365*24小时不间断运行,偶尔会出现系统死机的情况。为了应对这个问题,我在研究看门狗,但这次我想分享另一个在项目中用到的有趣方法:如何通过雷达点云和特定形状(90度)的反光板识别充电桩的坐标,实现机器人自动充电。
硬件和最终目标
我们的目标是利用雷达来识别安装在充电桩上的90度反光板,并确定其中心点坐标和朝向。以下是具体的实现方法:
1. 订阅雷达数据并转换成点云滤波
首先,我们需要订阅雷达数据,并筛选出反光强度较大的点,将其转换为点云并保存。
import rclpy from rclpy.node import Node from sensor_msgs.msg import LaserScan, PointCloud2, PointField import numpy as np import open3d as o3d def points_to_pointcloud2(points, frame_id): msg = PointCloud2() msg.header.frame_id = frame_id msg.height = 1 msg.width = len(points) msg.fields.append(PointField(name="x", offset=0, datatype=PointField.FLOAT32, count=1)) msg.fields.append(PointField(name="y", offset=4, datatype=PointField.FLOAT32, count=1)) msg.fields.append(PointField(name="z", offset=8, datatype=PointField.FLOAT32, count=1)) msg.is_bigendian = False msg.point_step = 12 msg.row_step = msg.point_step * len(points) msg.is_dense = False msg_data = [] for p in points: msg_data.append(p[0]) # x msg_data.append(p[1]) # y msg_data.append(p[2]) # z msg.data = np.array(msg_data, dtype=np.float32).tostring() return msg class ScanSubscriberPublisher(Node): def __init__(self): super().__init__('scan_subscriber_publisher') self.subscription = self.create_subscription( LaserScan, 'scan', self.scan_callback, 10) self.publisher_ = self.create_publisher(PointCloud2, 'scan_match', 10) self.threshold = 250 # 设置强度阈值 def scan_callback(self, msg): points = [] intensities = np.array(msg.intensities) ranges = np.array(msg.ranges) # 检查强度大于阈值的点 indices = np.where(intensities > self.threshold)[0] # 将符合条件的点添加到列表中 for i in indices: range_val = ranges[i] if range_val < msg.range_max and range_val > msg.range_min: angle = msg.angle_min + i * msg.angle_increment x = range_val * np.cos(angle) y = range_val * np.sin(angle) points.append([x, y, 0.0]) # 假设所有点都在平面上,z轴设为0 # 发布点云消息 cloud_msg = points_to_pointcloud2(points, msg.header.frame_id) self.publisher_.publish(cloud_msg) pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud() pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points) o3d.io.write_point_cloud("point_cloud.pcd", pcd) self.destroy_subscription(self.subscription) rclpy.shutdown() rclpy.get_global_executor().shutdown() def main(args=None): rclpy.init(args=args) node = ScanSubscriberPublisher() rclpy.spin(node) node.destroy_node() rclpy.shutdown() if __name__ == '__main__': main()在上面的代码中,我们订阅了雷达数据并筛选出反光强度较大的点,然后将这些点转换为点云并发布。同时,保存点云数据为文件,供后续处理使用。
2. 下采样和滤波
接下来,我们对点云数据进行下采样和滤波,以去除噪声点并减少计算量。
import numpy as np import open3d as o3d import time # Load point cloud data pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud('point_cloud.pcd', remove_nan_points=True, remove_infinite_points=True) start_time = time.time() # Radius filtering cl, index = pcd.remove_radius_outlier(nb_points=10, radius=0.2) new_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(index) # Downsampling voxel_size = 0.025 downsampled_pcd = new_pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size=voxel_size)在这段代码中,我们首先加载点云数据,并通过半径滤波去除孤立点。接着,对点云进行下采样,以减少计算量。
3. 提取点云趋势
我们需要将点云数据转换为极坐标系,以便更容易分析趋势。
# Convert point cloud to polar coordinates points = np.asarray(downsampled_pcd.points) r = np.sqrt(points[:, 0]**2 + points[:, 1]**2) theta = np.arctan2(points[:, 1], points[:, 0]) z = points[:, 2] # Construct polar point cloud and sort by angle polar_points = np.vstack((r, theta, z)).T sorted_indices = np.argsort(polar_points[:, 1]) sorted_polar_points = polar_points[sorted_indices] # Convert back to Cartesian coordinates cart_points = np.column_stack((r * np.cos(theta), r * np.sin(theta))) # Track distance changes distance_changes = np.diff(sorted_polar_points[:, 0]) direction_changes = np.sign(distance_changes) # Prepare data positive_points = [] negative_points = [] for i in range(len(direction_changes)): if direction_changes[i] > 0: positive_points.append(cart_points[sorted_indices[i], :2]) else: negative_points.append(cart_points[sorted_indices[i], :2]) # Convert lists to numpy arrays positive_points = np.array(positive_points) negative_points = np.array(negative_points)在这段代码中,我们将点云转换为极坐标系,并按照角度进行排序。接着,我们跟踪距离变化,并根据变化方向将点分为两类:正变化点和负变化点。
4. 拟合直线
使用RANSAC算法拟合直线,以找到反光板的边缘。
from sklearn.linear_model import RANSACRegressor def fit_line(points): if len(points) < 2: return None, None reg = RANSACRegressor().fit(points[:, 0].reshape(-1, 1), points[:, 1]) return reg, reg.estimator_.coef_[0], reg.estimator_.intercept_ pos_line, pos_slope, pos_intercept = fit_line(positive_points) neg_line, neg_slope, neg_intercept = fit_line(negative_points)在这段代码中,我们使用RANSAC算法拟合两条直线,分别对应正变化点和负变化点。
5. 计算斜率交点和夹角
通过计算两条直线的交点和夹角,确定反光板的中心点坐标和朝向。
import math # 计算交点 def find_intersection(k1, b1, k2, b2): if k1 == k2: return None # 平行或重合,无交点 x = (b2 - b1) / (k1 - k2) y = k1 * x + b1 return (x, y) # 计算夹角 def find_angle(k1, k2): tan_theta = abs((k1 - k2) / (1 + k1 * k2)) theta_radians = math.atan(tan_theta) theta_degrees = math.degrees(theta_radians) return theta_degrees intersection = find_intersection(pos_slope, pos_intercept, neg_slope, neg_intercept) angle = 180 - find_angle(pos_slope, neg_slope) # 计算与x轴的夹角 def angle_with_x_axis(k): theta_radians = math.atan(k) theta_degrees = math.degrees(theta_radians) return theta_degrees angle1 = angle_with_x_axis(pos_slope) angle2 = angle_with_x_axis(neg_slope) # 输出结果 station_angle = (angle1 + angle2) / 2 + 180 print(f"交点: {intersection}, 夹角: {angle}") print(f"充电桩坐标: {intersection}, 坐标夹角: {station_angle}")在这段代码中,我们计算了两条直线的交点、夹角以及相对于x轴的角度,得出了充电桩的坐标和朝向。
示例运行结果:
0.00625920295715332 交点: (0.4631433880355934, 0.004179420328549566), 夹角: 119.32425765226662 充电桩坐标: (0.4631433880355934, 0.004179420328549566), 坐标夹角: 175.068141321865946. 结果展示
最后,我们绘
制点云和拟合的直线,以可视化结果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # Plot the points and the fitted lines plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) plt.scatter(positive_points[:, 0], positive_points[:, 1], color='blue', label='Positive change points') plt.scatter(negative_points[:, 0], negative_points[:, 1], color='red', label='Negative change points') # Lines if pos_line: x_values = np.array([min(positive_points[:, 0]), max(positive_points[:, 0])]) y_values = pos_slope * x_values + pos_intercept plt.plot(x_values, y_values, color='cyan', label='Fitted line for positive points') if neg_line: x_values = np.array([min(negative_points[:, 0]), max(negative_points[:, 0])]) y_values = neg_slope * x_values + neg_intercept plt.plot(x_values, y_values, color='magenta', label='Fitted line for negative points') plt.xlabel('X Coordinate') plt.ylabel('Y Coordinate') plt.xlim(-1.0,1.0) plt.ylim(-1.0,1.0) plt.title('Point Cloud and Fitted Lines') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.show()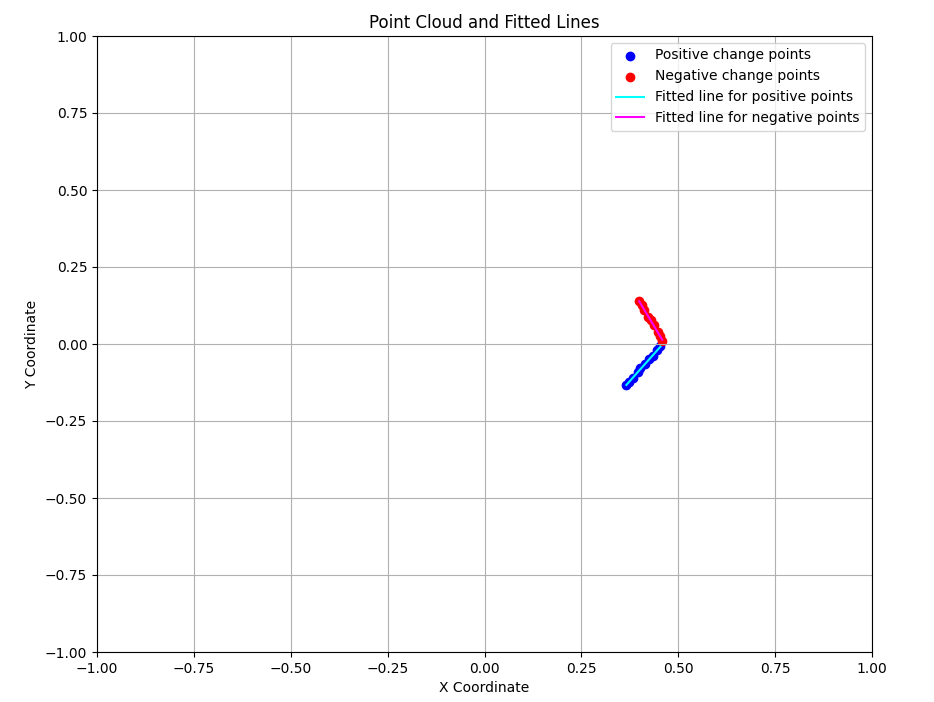
通过上述步骤,我们成功地通过雷达点云识别充电桩,并计算出了充电桩的坐标和朝向。这种方法在实际应用中能够有效地帮助机器人实现自动充电功能。
希望这篇文章对大家有所帮助,欢迎在下次有空的时候一起讨论看门狗的实现。谢谢大家!
-
您的ROS 2机器人自动充电项目听起来非常有趣且实用!通过雷达点云识别充电桩的方法不仅技术性强,而且为机器人实现自动充电功能提供了新的思路。下面我将根据您的描述,对您的项目方案进行进一步的解读和总结。
项目总结
您成功地通过雷达数据识别了充电桩上的90度反光板,并计算出了充电桩的中心点坐标和朝向。整个流程涵盖了从雷达数据订阅到点云处理、滤波、拟合直线以及最终坐标和角度计算的完整步骤。您还通过可视化工具展示了识别结果,使得整个流程更加直观。
关键点回顾
- 雷达数据订阅与转换:您首先订阅了雷达数据,并筛选出反光强度较大的点,将其转换为点云格式并保存。
- 点云下采样与滤波:为了去除噪声点并减少计算量,您使用了半径滤波和下采样技术对点云进行了处理。
- 点云趋势分析与直线拟合:您通过将点云转换为极坐标系并跟踪距离变化,成功地提取了点云的趋势。随后,使用RANSAC算法拟合了直线,以找到反光板的边缘。
- 坐标与角度计算:通过计算两条直线的交点和夹角,您得到了充电桩的中心点坐标和朝向。
- 结果展示:最后,您绘制了点云和拟合的直线,以可视化的方式展示了识别结果。
潜在优化与扩展
- 实时性优化:对于实时性要求较高的应用场景,可以考虑进一步优化算法,减少计算时间。
- 多传感器融合:可以结合其他传感器数据(如视觉、IMU等)进行多传感器融合,提高充电桩识别的准确性和稳定性。
- 鲁棒性增强:考虑在不同环境条件下(如光照变化、天气变化等)进行测试,以增强系统的鲁棒性。
- 自动充电路径规划:在识别到充电桩后,可以进一步实现机器人的自动充电路径规划,确保机器人能够安全、高效地到达充电桩进行充电。
结论
您的ROS 2机器人自动充电项目通过雷达点云识别充电桩的方法,为机器人实现自动充电功能提供了一种有效的解决方案。整个项目流程清晰、技术性强,且具有一定的实用性和创新性。期待您在未来能够继续探索和优化这一方案,为机器人领域的发展做出更多贡献!
以上为生成回答,仅供参考~